With its vast population, growing economy, and increasing size, the Chinese game market is too big and lucrative to ignore. But it’s not a free range where the game companies can barge in and start making profits. With licensing, monetization restrictions, and even restrictions on children’s access to games, it’s a tough market to navigate.
These restrictions create a tough market even for domestic companies, let alone foreign companies trying to enter or survive in the market, and the Chinese market is home to multiple worldwide giants.
Developments in such a vast market with multiple worldwide companies cannot be taken as isolated events with confined results. In the end, regardless of the industry, what happens in China concerns the whole world. China has some of the biggest game companies in the world. Even the domestic ones are huge on a worldwide scale, and if you corner a beast, you shouldn’t be surprised when it becomes aggressive. That’s why it’s essential to understand what’s going on in the Chinese game market and how it may affect the rest of the world.
Market: Facts & Stats
An overview of the Chinese game market
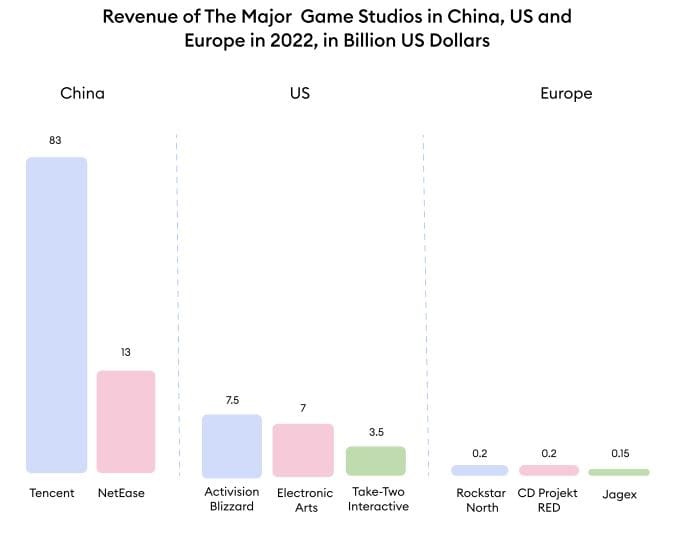
The Chinese game industry is a juggernaut, boasting the world’s highest revenue at $45.5 billion in 2022 and 664 million gamers. But it’s not just about its size; it’s also about its unique characteristics and impact on the global stage. Unlike many markets, mobile games dominate China, accounting for over 76% of total gaming revenue. This has fueled the success of companies like Tencent and NetEase, which specialize in mobile titles.

With a population exceeding 1.4 billion and a growing middle class with disposable income, China represents one of the most lucrative gaming markets in the world. The Chinese game industry has experienced exponential growth, driven by increasing smartphone penetration, expanding internet infrastructure, and a burgeoning esports scene. This growth has attracted domestic and international gaming companies eager to tap into this vast market and capitalize on its immense potential for revenue generation.

However, alongside its remarkable growth, the Chinese game industry is also subject to a complex regulatory landscape shaped by government policies and cultural considerations. In recent years, the Chinese government has implemented various regulatory measures aimed at addressing concerns such as gaming addiction among minors, ensuring the integrity of gaming content, and promoting healthier gaming habits.
These regulatory circumstances have significant implications for the domestic and global gaming markets. Considering China’s position in the worldwide gaming ecosystem, shifts in its regulatory landscape can affect international markets dramatically.
Purposes of the regulatory restrictions on the Chinese game industry
Chinese game industry has been subject to increasingly stringent regulatory measures intended to address various societal concerns. While intended to promote a healthier gaming environment, these regulations have significantly affected market dynamics and the operations of gaming companies in China.

Addressing Gaming Addiction
With concerns about the negative impact of excessive gaming on children’s physical and mental well-being, the government has implemented measures to combat gaming addiction. Restrictions on gaming time for minors, limitations on in-game spending, and the prohibition of certain reward mechanisms aim to promote healthier gaming habits among young players.
Ensuring Content Compliance
Chinese regulators are keen on ensuring that gaming content aligns with cultural values, political sensitivities, and moral standards deemed appropriate by the authorities. This includes censoring violence, explicit content, and politically sensitive themes and mandating that game servers be located within China to safeguard user data.
Promoting Social Harmony
Regulatory measures also aim to promote social harmony and stability by addressing concerns about online behavior, cyberbullying, and the spread of harmful ideologies through gaming platforms. Advertisements for games must comply with requirements for building a Socialist Spiritual Civilization, reflecting the government’s broader ideological objectives.
Effects of the regulatory restrictions on the Chinese game industry
Market Impact
The announcement of new regulations has led to significant market volatility, with shares in major Chinese gaming companies such as Tencent and NetEase experiencing sharp declines. Investors have responded with concern, resulting in a collective loss of nearly $80 billion in market value from these companies.
Revenue Decline
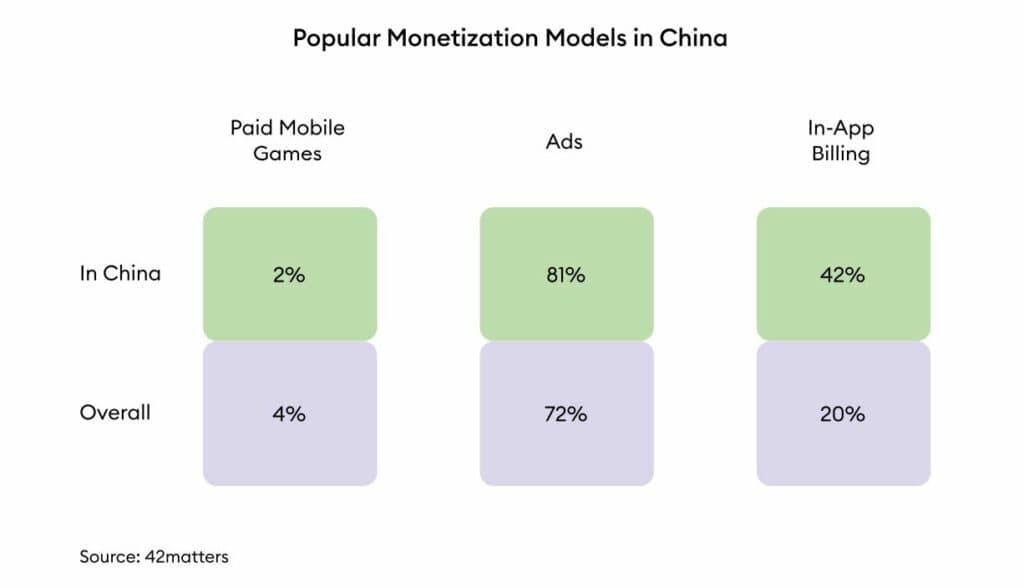
The regulatory restrictions have impacted revenue streams for gaming companies, particularly those reliant on in-game purchases and virtual goods sales. Restrictions on spending limits and reward mechanisms have led to declines in revenue growth, forcing companies to explore alternative monetization models.
Market Consolidation and Restructuring
The stringent regulatory environment has prompted consolidation and restructuring within the game industry as companies seek to navigate the challenges of regulatory restrictions. Some companies have merged or formed strategic partnerships to strengthen their position in the market, while others have diversified into other areas to compensate for potential revenue losses.
While the regulatory restrictions imposed on the Chinese game industry are intended to address legitimate societal concerns, they have profoundly affected market dynamics and gaming companies’ operations.
Chinese restrictions compared to the restrictions imposed in other countries
In contrast to China’s focus on social harmony and gaming addiction, regulatory frameworks in Western countries like England and France prioritize consumer protection, content regulation, and industry transparency.
Age Ratings and Content Classification
England and France have robust systems for age ratings and content classification, ensuring that games are appropriately labeled to inform consumers about their suitability for different age groups. Regulatory bodies such as the British Board of Film Classification (BBFC) and the Pan European Game Information (PEGI) provide age ratings and content descriptors for games.
Protection of Minors
While England and France have regulations that seek to protect minors from harmful content and excessive spending, such as parental controls and age verification mechanisms, these measures are less stringent compared to China’s playtime limits and spending restrictions.
Consumer Rights and Data Protection
Gaming regulations in England and France prioritize consumer rights, data protection, and privacy. Companies must comply with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, ensuring that players’ personal information is handled responsibly and transparently.
Generally, while China’s regulations prioritize social harmony and gaming addiction prevention and ensuring and protecting the government’s ideology, future, and interests, England and France focus on consumer protection, content regulation, and data privacy. Understanding these differences is essential for gaming companies operating in multiple markets to comply with regulatory requirements and adapt their strategies accordingly.
How Chinese game companies compensate for the domestic restrictions?
As regulatory restrictions tighten within the Chinese game industry, Chinese-based gaming companies increasingly look to international markets to counteract domestic challenges and sustain growth. Facing constraints on in-game spending, content compliance, and market saturation at home, these companies are expanding their presence abroad, leveraging their expertise, resources, and market dominance to capture new opportunities and diversify their revenue streams.
In response to these domestic challenges, Chinese-based gaming companies turn their attention to international markets, where they see untapped opportunities for growth and expansion:
Market Diversification
Expanding into international markets allows Chinese gaming companies to diversify their revenue streams and reduce dependence on the volatile domestic market. By targeting regions with less stringent regulatory environments and higher spending power, these companies can mitigate risks associated with domestic restrictions and market saturation.
Access to New Audiences
International expansion provides Chinese gaming companies with access to new audiences and user demographics. By localizing content, adapting marketing strategies, and understanding cultural preferences, these companies can attract and retain international players, driving user engagement and monetization.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Chinese gaming companies actively pursue strategic acquisitions and partnerships to facilitate international expansion efforts. Investing in or acquiring foreign gaming studios, distribution platforms, and technology companies can accelerate their global growth strategies and gain a competitive edge in international markets.
Turning to remakes to bypass licensing
The Chinese government takes advantage of licenses to maintain its iron grip on the game industry. The government gradually decreases the number of new licenses and even sometimes completely halts issuing new ones. This forces the game companies in China to turn to remakes to bypass the licensing issue. Remakes are a quick, risk-free and smart solution in short term but it has the risk of driving the industry to aridity and repetition.
Chinese game companies may resort to more aggressive expansion strategies
Chinese-based gaming companies may adopt more aggressive expansion strategies to capitalize on international opportunities and rectify domestic restrictions:
Investments in Overseas Studios
Chinese gaming companies invest in overseas studios to access local talent, expertise, and intellectual property. By acquiring foreign studios, these companies can expand their content portfolio, accelerate game development cycles, and strengthen their position in international markets. Tencent and NetEase have been utilizing this strategy for years.
Global Publishing and Distribution Partnerships
Chinese gaming companies are forming strategic partnerships with global publishing and distribution platforms to expand their reach and maximize market penetration. These companies can effectively promote and monetize their games in international markets by leveraging established distribution networks and marketing channels.
Localized Content Development
Chinese gaming companies are investing in localized content development to cater to the preferences and tastes of international audiences. These companies can enhance player engagement and retention in global markets by adapting game themes, art styles, and gameplay mechanics to suit different cultural contexts. A good example of this would be the partnership between Blizzard and NetEase.
Comparison of Chinese and foreign companies in the face of restrictions: Advantages and disadvantages
Eastern and Western markets have unique challenges. While most eastern markets, like Japan, pose distinct cultural challenges, Western game markets are more sensitive about data privacy, consumer rights, and the protection of minors.
China has a unique position among all markets, not merely because of its size and potential but because of the authority ruling the country. It can be debated if China has a totalitarian government or not. Still, it’s a one-party state where applications like social credit systems are in effect through extensive surveillance and tracking systems that monitor people at the individual level. It can even be argued that auto-censoring have become a reflex of the game industry in China to an extent that industry sometimes self-imposes restrictions.
Unlike in Western countries, it’s almost impossible and may have dire consequences to resort to using loopholes or operating in grey areas in the jurisdiction of such a government. Therefore, it can be assumed that Chinese companies have adapted better to strict restrictions.
It can be metaphorized as foreign companies trying to walk in tighter shoes when trying to get into the Chinese market and the Chinese companies doing the opposite. Both situations are not ideal, but adapting to fewer restrictions and operating under a non-one-party state is obviously preferable. Chinese companies have the advantage of vast financial resources along with an enormous domestic market which they are used to operating within.
NEXT: Why did Apple’s new App Store policy create a backlash from the industry?






